Products
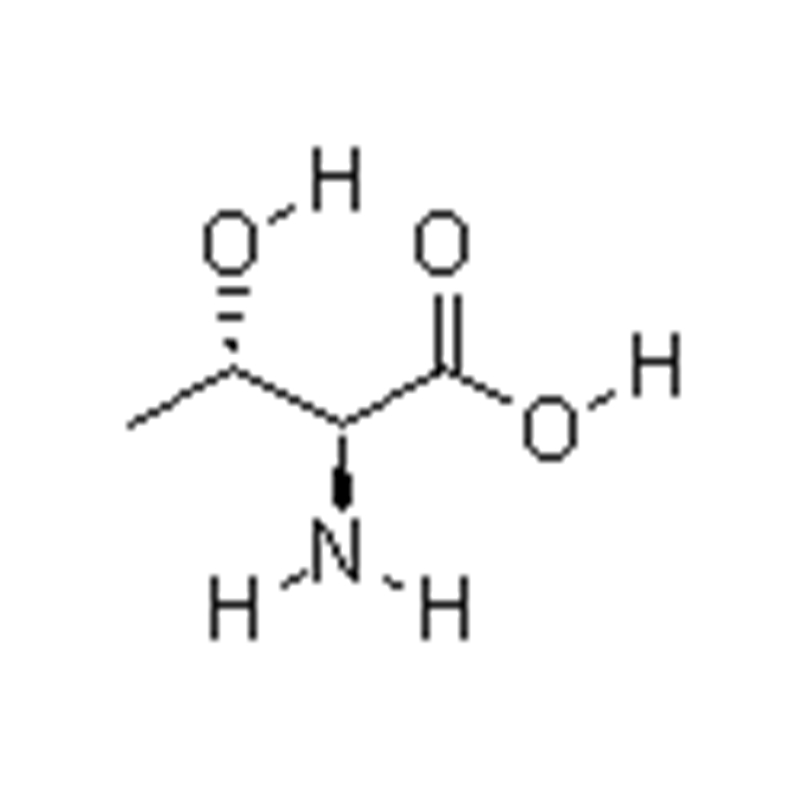
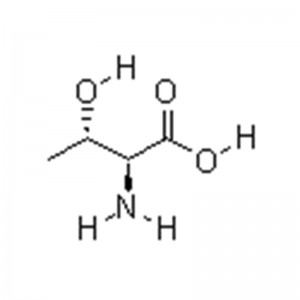
L-threonine
Description
a. It is mainly used as a nutritional supplement. Co heating with glucose is easy to produce burnt and chocolate flavor, which can enhance flavor. It can also be used in biochemical research.
b. Threonine is an essential amino acid as a feed nutrient fortifier. Threonine is often added to the feed of juvenile piglets and poultry. It is the second limiting amino acid of pig feed and the third limiting amino acid of poultry feed. It is added to the feed mainly composed of wheat, barley and other grains.
c. Nutritional additive, also used to prepare amino acid infusion and comprehensive amino acid preparation.
d. It is used for auxiliary treatment of peptic ulcer. It can also treat anemia, angina pectoris, arteritis, cardiac insufficiency and other cardiovascular diseases.
e. Threonine (L-threonine) was isolated and identified from fibrin hydrolysate by W. C. rose in 1935. It has been proved to be the last essential amino acid discovered. It is the second or third limiting amino acid of livestock and poultry. It plays an extremely important physiological role in animals. Such as promoting growth and improving immune function; Balance the amino acids in the diet to make the ratio of amino acids closer to the ideal protein, so as to reduce the requirements of livestock and poultry for the protein content in the feed. Lack of threonine can lead to decreased food intake, growth inhibition, decreased feed utilization, immune function inhibition and other symptoms. In recent years, lysine and methionine synthetics have been widely used in feeds. Threonine has gradually become a limiting factor affecting animal production performance. Further research on threonine will help to effectively guide livestock and poultry production.
f. Threonine (L-threonine) is an amino acid that animals can not synthesize but need. It can be used to accurately balance the amino acid composition of feed, meet the needs of animal growth and maintenance, improve weight gain and lean meat rate, and reduce feed meat ratio; It can improve the nutritional value of feed materials with low amino acid digestibility and improve the production performance of low-energy feed; It can reduce the level of crude protein in feed, improve the utilization rate of feed nitrogen and reduce feed cost; It can be used for raising pigs, chickens, ducks and high-grade aquatic products. L-threonine is a feed additive produced by deep liquid fermentation and refining with corn starch and other raw materials based on the principle of bioengineering. It can adjust the amino acid balance in the feed, promote growth, improve meat quality, improve the nutritional value of feed raw materials with low amino acid digestibility, and produce low protein feed, which helps to save protein resources, reduce the cost of feed raw materials, reduce the nitrogen content in livestock and poultry feces and urine, and the ammonia concentration and release rate in livestock and poultry houses. It is widely used to add piglet feed, breeding pig feed, broiler feed, shrimp feed and eel feed.
g. Threonine (L-threonine) is the only amino acid that does not undergo deamination and transamination in the catabolism of the body, but is directly converted into other substances through the catalysis of threonine dehydratase, threonine dehydrogenase and threonine aldolase. For example, threonine can be converted into butyryl coenzyme A, succinyl coenzyme A, serine, glycine, etc. In addition, excessive threonine can increase lysine- α- The activity of ketoglucose reductase. Adding proper amount of threonine to the diet can eliminate the decrease of body weight gain caused by excessive lysine, and the decrease of protein / deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and RNA /dna ratio in liver and muscle tissue. Addition of threonine can also reduce the growth inhibition caused by excessive tryptophan or methionine. It is reported that most of the absorption of threonine in chickens is in the duodenum, crop and glandular stomach. After absorption, threonine is rapidly transformed into liver protein and deposited in the body.
Product Info
Cas No. :72-19-5
Purity :≥98.5%
Formula :C4H9NO3
Formula Wt. :119.1192
Chemical Name:L-hydroxybutyric acid; α- Amino group- β- Hydroxybutyric acid; 2s, 3R) - 2-amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid; Threonine; H-Thr-OH
IUPAC Name :L-hydroxybutyric acid; α- Amino group- β- Hydroxybutyric acid; 2s, 3R) - 2-amino-3-hydroxybutyric acid; Threonine; H-Thr-OH
Melting Point :256(dec.)(lit.)
Solubility :Soluble in water (200g/l, 25 ℃), insoluble in methanol, ethanol, ether and chloroform.
Appearance :White crystal or crystalline powder, containing 1/2 crystal water. Odorless, slightly sweet.
Shipping and Storage
Store Temp:Closed package in brown wide mouth glass bottle. Store in a cool and dry place away from light.
Ship Temp:Sealed, cool and leak proof.
References
1. Xuqingyang, fengzhibin, sunyuhua, etc Effect of dissolved oxygen on L-threonine fermentation. CNKI; Wanfang, 2007
2. Fengzhibin, wangdongyang, xuqingyang, etc Effect of nitrogen source on L-threonine fermentation. Chinese Journal of bioengineering, 2006