Products
Ribonucleic Acid
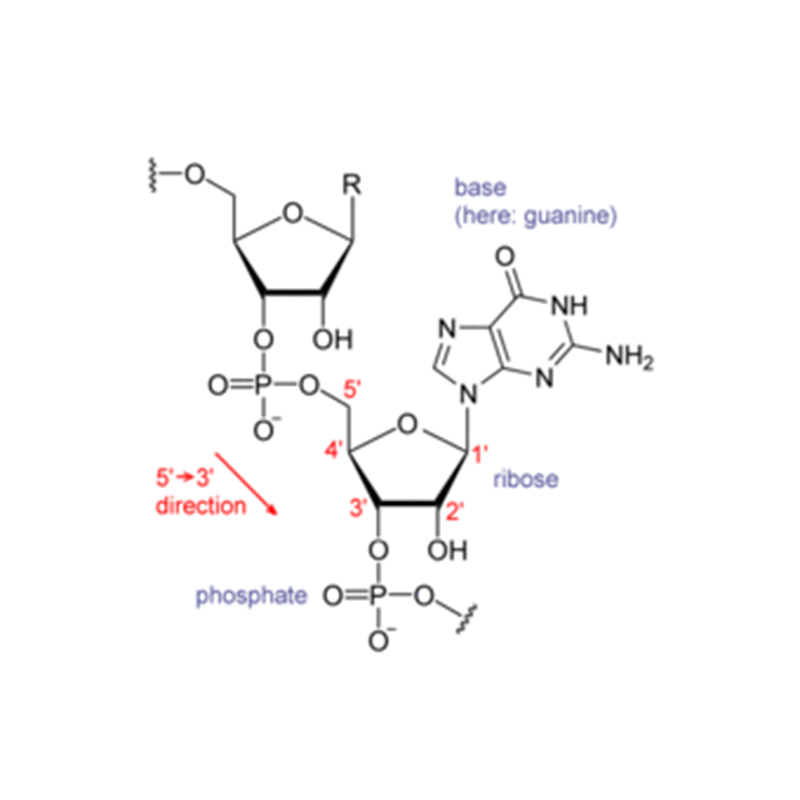
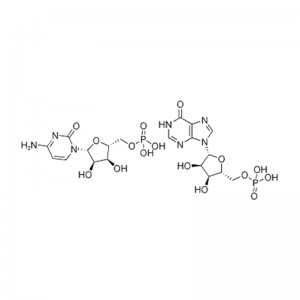
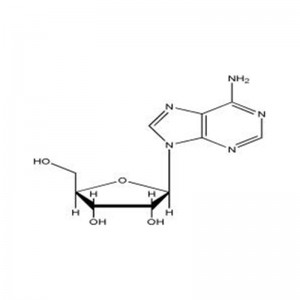
Structural Formula
Physical
Appearance: white or light yellow powder
Density.
Melting point.
Boiling point.
Refractivity
Flash point.
Safety Data
Hazardous category.
Dangerous Goods Transport Number.
Packing category.
Application
RNA and DNA are used as medicine. People take RNA/DNA combinations to improve memory and mental sharpness, treat or prevent Alzheimer's disease, treat depression, increase energy, tighten skin, increase sex drive, and counteract the effects of aging.
RNA (abbreviated as RNA, Ribonucleic Acid) is a carrier of genetic information found in living cells and in some viruses and virus-like organisms.RNA consists of ribonucleotides condensed by phosphodiester bonds to form long chain-like molecules. A ribonucleic acid molecule consists of phosphate, ribose and bases. there are four main types of bases in RNA, namely A (adenine), G (guanine), C (cytosine) and U (uracil), where U (uracil) replaces T (thymine) in DNA. The role of RNA in the body is mainly to direct the synthesis of proteins.
One cell in the human body contains about 10 pg of RNA (containing about 7 pg of DNA). Compared with DNA, RNA has a wide variety, small molecular weight and large variation in content.RNA can be divided into messenger RNA and non-coding RNA according to structure and function.Non-coding RNA is divided into non-coding large RNA and non-coding small RNA.Non-coding large RNA includes ribosomal RNA, long chain non-coding RNA.Non-coding small RNA includes transfer RNA, nuclease, small molecule RNA, etc. . Small molecule RNA (20~300nt) includes miRNA, SiRNA, piRNA, scRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, etc. Bacteria also have small molecule RNA (50~500nt).
RNA, like DNA, is also a polynucleotide chain composed of various nucleotides linked by 3′,5′-phosphodiester bonds, but differs from DNA in a number of ways.